A Guide to Understand Plant Cell with Diagram
Plants and animal cells have different structures, and the functions of the organelles also vary from each other. Therefore, if a student wants to have a comparative study on plant and animal cells, the plant cell functions, they need to use a plant cell diagram. Creating a plant cell diagram by hand can be difficult, and therefore the students must use the EdrawMax Online tool, which can help them have a high-quality plant cell diagram.
1. The Plant Cell
Cells are the structural and functional unit of any living being. Plants mainly have eukaryotic cells surrounded by cell walls. Plant cells also have a nucleus and several other organelles, which are associated with different body functions of plants.

1.1 The Structure of a Plant Cell
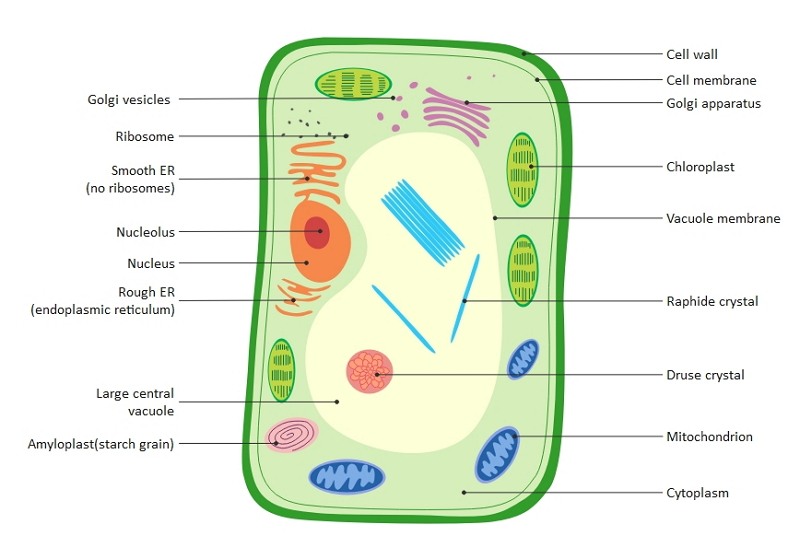
Cell wall:
In plant cells, there is a rigid layer of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, pectin, glycoproteins present outside the cell membrane. They have three layers, primary, secondary and middle lamella. The main function of the cell wall is to give mechanical rigidity to the cell and protect it.
Cell membrane:
There is a semi-permeable cell membrane that covers the cell. It consists of layers of protein and lipids. Their semi-permeable nature prevents toxic materials from going into the cell while allowing minerals and nutrients to get in the cell.
Nucleus:
The nucleus is the carrier of genetic information in Eukaryotic cells. They are membrane-bound and contain DNA. These DNAs are essential for cell division and the growth of the organism. The nucleus has a nucleolus that participates in the production of ribosomes and the protein-producing mechanisms. There are pores on the nuclear membrane for the passing of the protein and nucleic acid.
Plastids:
Plastids are membrane-bound organelle with DNA. They store starch for photosynthesis and also synthesize some of the molecules like fatty acids. Plastids can be of different types, and they have various functions:
- Leucoplasts: Leucoplasts are colorless, non-photosynthetic plastids present in roots, seeds, and tubers. Their primary function is to store protein, lipids, and scratches.
- Chloroplasts: These are disc-shaped organelles and are covered with a phospholipid membrane. The green color pigment chlorophyll is present in the chloroplasts, a must for the photosynthesis process. In the presence of light energy, chlorophyll transforms the water and carbon dioxide into glucose.
- Chromoplasts: These are colored plastids. They participate in the synthesis of pigments. They can be red, orange, or yellow in color and are responsible for the color of ripe fruits and flowers.
Central vacuole:
Central vacuole is a big vacuole present in the plant cell, taking almost 30% of the same. It stores water and then controls the turgor pressure. It pushes the cell contents towards the cell membrane, which helps the plant cell to get more light for photosynthesis. This central vacuole has cell sap.
Golgi apparatus:
Golgi apparatus is present in the eukaryotic cells, and there can be hundreds of them present in the plant cells. They take part in the modification and transportation of protein and lipids as they get exported to the cells.
Ribosomes:
Ribosomes are membrane-bound organelles made with RNA and protein. It works as the site of protein synthesis. Therefore, these smallest organelles are called the protein factories of the cells.
Mitochondria:
Mitochondria is a double-membraned organelle present in the eukaryotic cells. They are known as the ‘Powerhouse of the cell’ as they break down carbohydrate molecules and generate energy.
Lysosomes:
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles known as suicidal bags. They have digestive enzymes allowing worn-out organelles' digestion and alien elements present in the cell. They also participate in the disposal of waste products.
 Source:EdrawMax Online
Source:EdrawMax Online
2. How to Draw the Plant Cell Diagram?
To understand the plant cell, the students may use a plant cell diagram that can make the learning smoother.
2.1 How to Create Plant Cell Diagram from Sketch
The students can draw a plant cell diagram by hand. However, there are different organelles and other structures, which can make it challenging enough. The students can follow these steps to create a plant cell diagram:
Step 1: To start with the plant cell diagram, the students need to draw a hexagon and draw straight lines from the hexagon's corner. Then double-line the whole structure. The extreme outer line is called the cell wall.
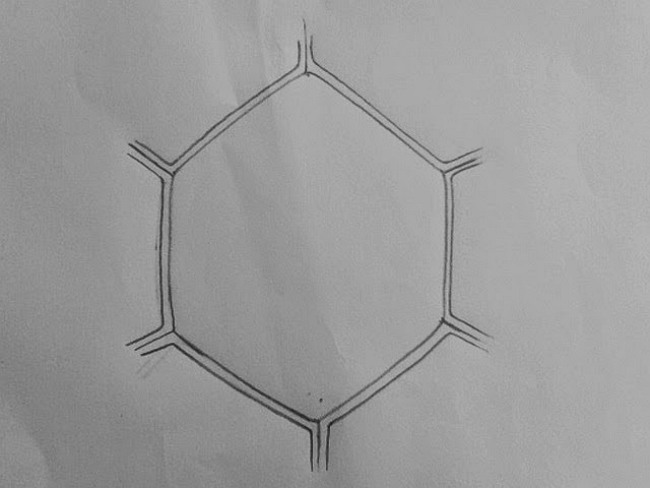
Step 2: The corners now look like pipes, and the students have to separate them into two parts and join with the rest of the double-lined structure. Then they need to round the new corners and shade them. Now the inner part of the hexagon is double-lined again. The inner layer is known as the middle lamella.
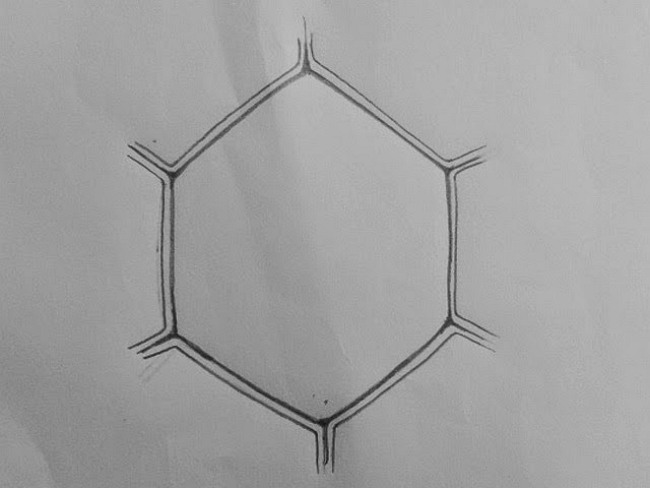
Step 3: Now, the students need to draw vacuoles. To make vacuoles, the students need to draw irregularly shaped circles. There is a big circle that represents the tonoplast.
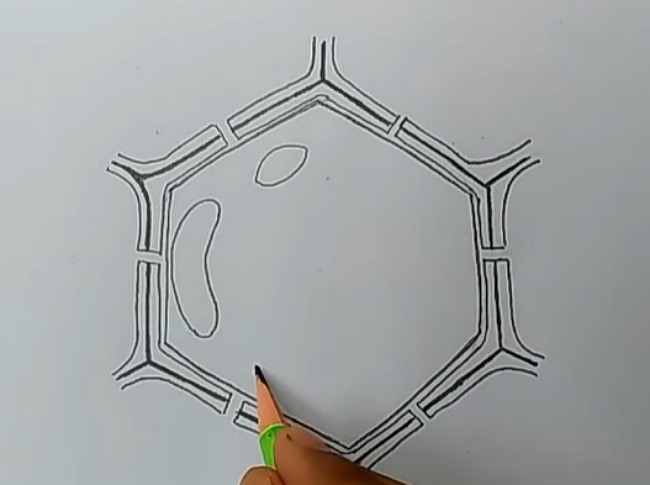
Step 4: After that, they need to draw a double-lined circle inside the hexagon. The double lines are removed at some places. Then there is a small shaded circle created inside the previous one. Fill the blank space of the same with thin string-shaped structures.
Step 5: From the outside of the nucleus, create some finger-like structures. They are the endoplasmic reticulum. Create some of these structures inside the cytoplasm. Draw dots on some of the endoplasmic reticulums. They need to draw some small droplets or tiny round structures inside the hexagon.
Step 6: To draw mitochondria, the students need to draw oval shapes, and then they have to double-line the outer cover. They need to create wavy double lines inside the structure.
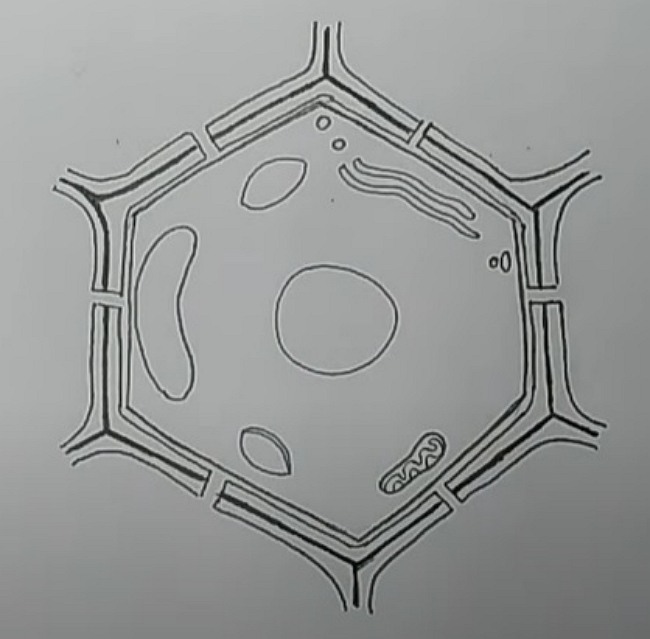
Step 7: They need to draw some circles with clusters of small dots, called the plastids. The whole blank part inside the hexagon is dotted, which is the cytoplasm of the cell.
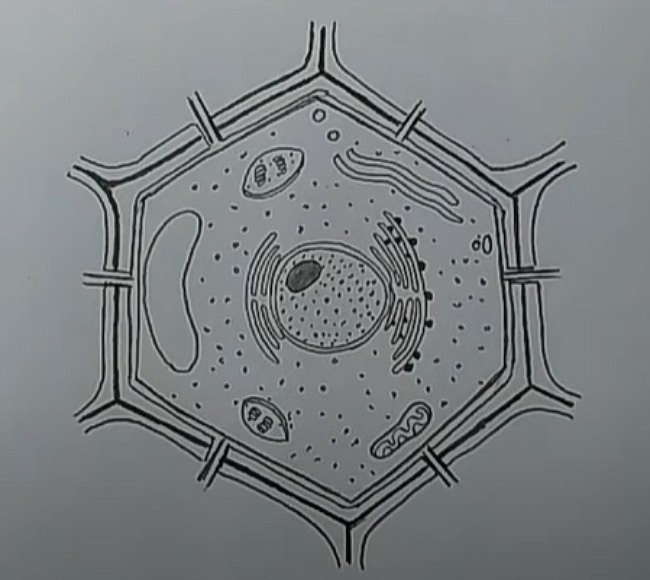
2.2 How to Create Plant Cell Diagram Online
However, creating a plant cell diagram by hand is difficult. It is time-consuming, and the students may not get satisfied with the diagram. The students can use EdrawMax Online to avoid the situation and can create a high-quality plant cell diagram. Here are a few simple steps which they can follow:
Step 1: EdrawMax Online is a user-friendly tool, and anyone can use it without any prior experience. To start with the process, they need to open the EdrawMax Online and then open New. Then they have to select the Science and Education option. The students can get multiple Science and Education related diagrams that they can use for their lessons.
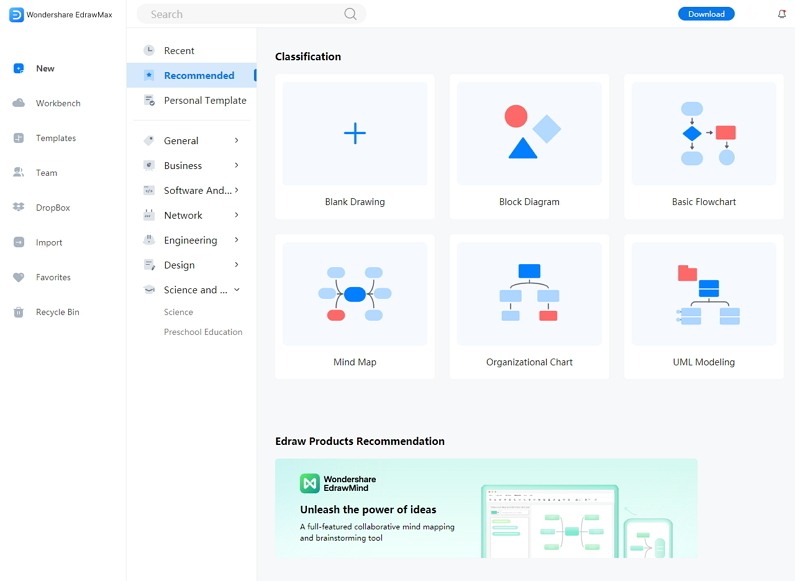
Step 2: They can choose the Biology option where they can find high-quality plant cell diagrams. They can modify the plant cell diagram as per their choice. It can help them to generate a perfect diagram for their lessons, projects, and dissertation papers.
Step 3: After selecting the template they require, the students should modify it as per their choice. The tool gives the students some hassle-free options to edit their diagrams. They can work on those images according to their preference to create a high-quality plant cell image.
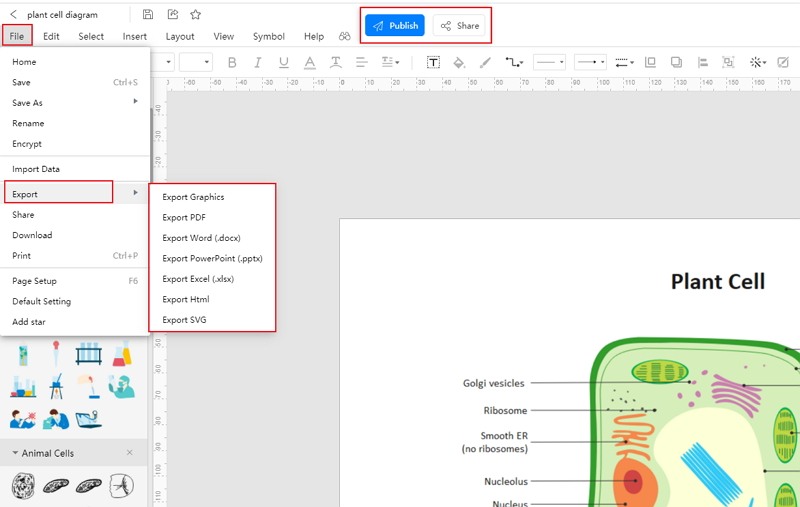
Step 4: Once the student completes their diagram, they can save it in multiple formats. They can also export them to use in their papers.
3. Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell
Though both plants and animals have cells as their structural and functional units, there are certain similarities and differences between these two types of cells:
- In the case of plant cells, it stores energy in starch form. In Animal cells, the energy is stored in the form of complex carbohydrate glycogen.
- Plants cells have cell walls made of cellulose. The animal cells do not have any cell walls.
- Planet cells generally don't have centriole and cilia, while animal cells have both of them.
- Plant cells have plastids with chloroplasts for photosynthesis. The animal cells don't have plastids.
- Plant cells have large central vacuoles called tonoplasts. The animal cells have small vacuoles but many in number.
4. Conclusion
Plant cells are structured so that they can get protected from external threats. The presence of chloroplasts makes them the primary producer. To learn about plant cells, the students must use a plant cell diagram. They can create a diagram by hand, which is a time-consuming process. They must use the EdrawMax Online tool to create a high-quality plant cell diagram.
In conclusion, EdrawMax Online is a quick-start diagramming tool, which is easier to make flower diagram and any 280 types of diagrams. Also, it contains substantial built-in templates that you can use for free, or share your science diagrams with others in our template community.