What is A Decision Tree with Examples
Create a Decision Tree on Edraw.AI Online Free Free Download Free Download Free Download Free DownloadWhat is a Decision Tree?
At first, a decision tree appears as a tree-like structure with different nodes and branches. When you look a bit closer, you would realize that it has dissected a problem or a situation in detail. It is based on the classification principles that predict the outcome of a decision, leading to different branches of a tree. It starts from a root, which gradually has different decision nodes. The structure has terminating nodes in the end.
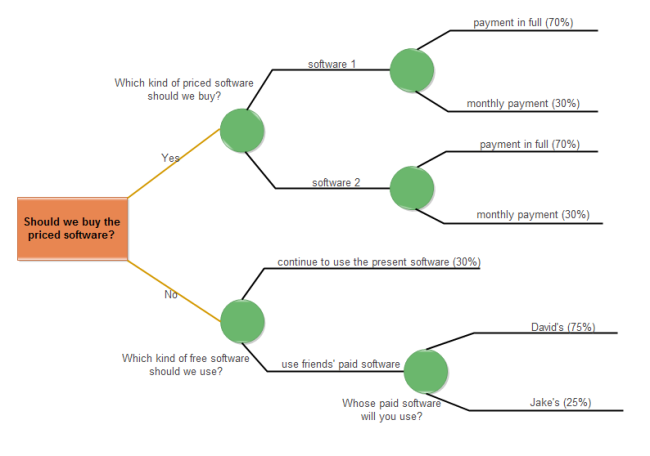
Ideally, a decision tree can be used in almost every sector. This is because we can take any real-world or hypothetical instance and represent it using a decision tree diagram. To further understand what a decision tree is, let’s consider this example. It asks a simple question – whether to buy a new software or not. If we buy a new tool, then it further leads to the comparison between the two options. If not, then we can either continue using the present software or borrow a friend’s tool.
Why do we need a Decision Tree?
Since a decision tree provides a systematic map of the present scenario and the available options, it certainly has a wide range of applications. Following are some of the advantages and reasons for using a decision tree diagram.
- With the help of these tree diagrams, we can resolve a problem by covering all the possible aspects.
- It plays a crucial role in decision-making by helping us weigh the pros and cons of different options as well as their long-term impact.
- No computation is needed to create a decision tree, which makes them universal to every sector.
- These prediction tree diagrams can be used to represent all kinds of categorical as well as continuous scenarios that can be tough to depict otherwise.
- In the present scenario, decision trees play a vital role in futuristic technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence.
- They can represent both quantitative as well as qualitative data in a visually appealing manner and that too without applying too much computation.
One of the best parts about decision tree diagrams is that they are extremely easy to make and will not require extensive training. We will explore some decision tree examples and major symbols in the next section to teach you how to create your first decision tree.
Major Symbols of a Decision Tree
After learning what is a decision tree and its importance, let’s dive into the details. Even if you have never worked on a classification model like this, you can easily learn how to draw a decision tree diagram. To do this, you need to be familiar with the major symbols that are used in a decision tree.
Decision node
This indicates a situation when a decision has to be made and is represented by a closed square. This is how most of the decision tree diagrams start.

Chance node
Whenever we are uncertain about the outcome of a situation, we represent it with a chance node. It can lead to multiple outcomes, but mostly it is recommended to just lead to two results at once. It is represented by a circle.

End node
These are the leaf nodes that represent the end of the decision diagram. No further branches are expected from an end node. A small triangle is used for a terminator or end node.

Branches
Every time a decision is made, it leads to different nodes. A branch would connect these nodes and represent a situation or a result. Mostly, the result is written over the branch in normal text.
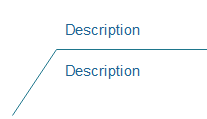
Rejected option
This is an optional symbol in a decision tree which is drawn after the entire diagram has been created. We simply mark it over the branch of the option that we wish to no longer continue.

How does Decision Tree Work - Learn From Examples
By now, you would be able to understand what is a decision tree and its major symbols. To further learn about their working and application, let’s consider a few decision tree examples. In this way, you can understand how a decision tree can play a crucial role in different scenarios.
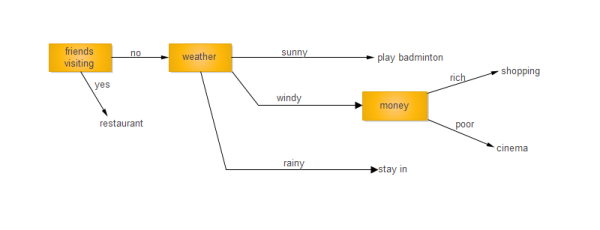
Let’s start with a basic decision tree about planning the events of the day. As you can see, if a friend would visit, then we can just visit a restaurant. If not, then it would depend on the weather. If it is rainy, then it is better to stay indoors while on a sunny day, we can go out and play. In case if, it is windy, and then we can, go either shopping or movies, depending on the available money.
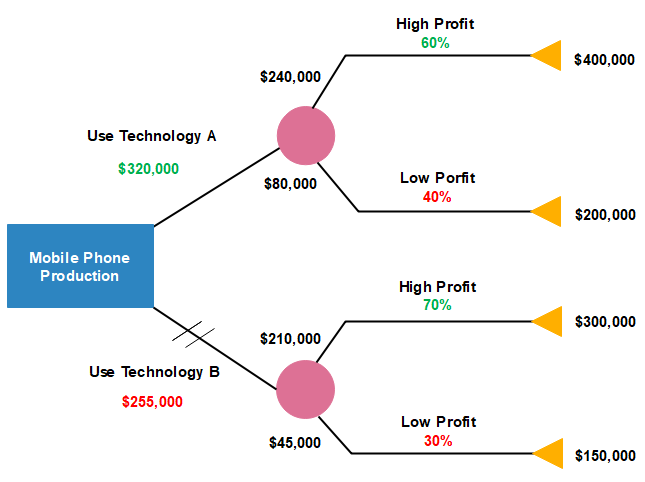
This is a more advanced decision tree in which we will explore the options for mobile phone production. Each of the units has their high and low profit margins. In the end, we can see the terminator nodes with their results. On the basis of that, Technology A has been chosen while Technology B has been rejected.
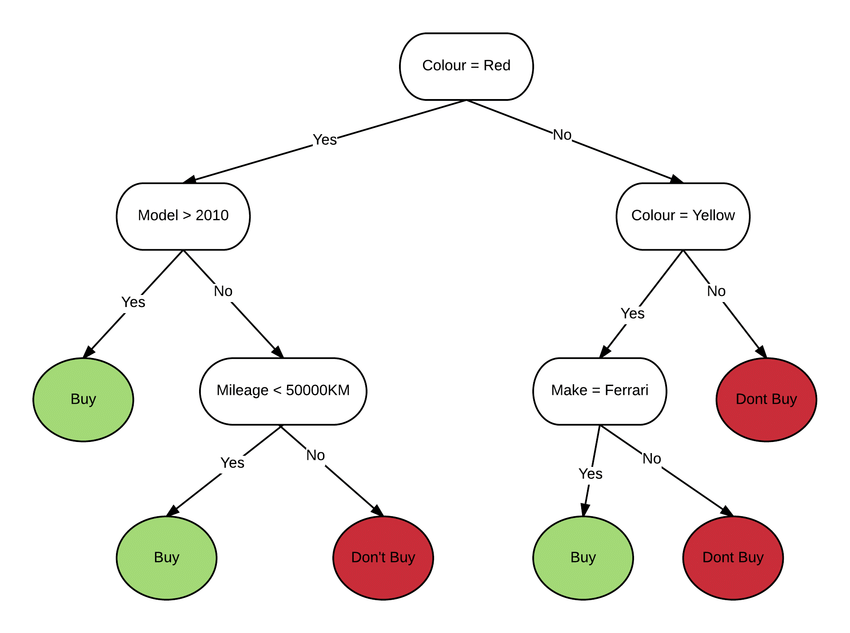
As you can see, most of the decision tree examples are related to real-life problems and their visual representation. In this, we will consider a person’s preference for buying a car. If the color is red, then further constrains like built year and mileage is considered. If not, then the brand of the vehicle is kept in mind. Wherever these conditions are not met, the car is not bought. On the other hand, it would be bought if it is red and newer than 2010, red car with good mileage, or a yellow Ferrari.
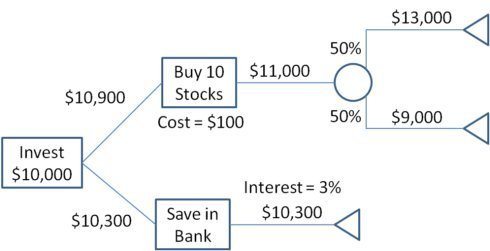
This is another one of those decision tree examples that we face in real-world on a frequent basis. In this, we will consider different options for investing money. If we just keep it in the savings account, then we will get a certain return. Another option involves investing money in stocks while further dividing it into two sources by half. Since the return from the stocks is more, it seems like a better investment option.
EdrawMax: Excellent Decision Tree Maker
If you are looking for a dedicated tool to draw all kinds of decision tree diagrams, then EdrawMax would be an ideal pick. It is extremely easy to use with a friendly interface. Therefore, you don’t need any prior technical experience to create decision trees with it.
- There are readily available templates in EdrawMax (even for decision tree) that users can pick and save their time in editing.
- There are 50000+ vectors in the tool that can help us design different diagrams like a professional.
- You can save your work on the cloud or even export it to all kinds of supported file formats.
- There are more than 260 different diagram types that the application supports presently.
- It is available for all the leading platforms and versions of Windows, Mac, and Linux.
One of the best parts about EdrawMax is the application offers a free trial version. Therefore, even if you are not sure about it, you can get a hands-on experience of the tool for free.
How to create a Decision Tree with EdrawMax?
As you can see, EdrawMax offers so many features to create professional-looking decision trees in less time. Here’s how you can also do the same using this resourceful tool.
In order to start with, you need to identify what problem you have and what is the available environment.
Try to create a map in your mind or at least identify the first decision that you wish to make. For instance, if you are buying a car, then you can think of the color you want to pick. You can come up with several other decisions that you would be taking to branch out the tree.
After having everything ready, launch EdrawMax to draw your decision tree. You can start with a blank canvas or simply pick the decision tree template under project management to save your time.
This will load all kinds of related vectors on the sidebar that you can pick. Just drag and drop the decision node, chance node, branches, or any other available vector to give your thoughts a visual representation.
Once you have created the basic structure of the decision tree diagram, you can format it the way you like. The application will let you change its size, background, color, edit text, and do so much more. In the end, you can just export the recently created decision tree in the format of your choice.
There you go! After reading this in-depth guide, you would be able to understand what a decision tree is, what its major symbols are, and how to create one using EdrawMax. For your convenience, we have also included some decision tree examples so that you can relate to these real-time scenarios. While decision trees are certainly helpful, they can sometimes lack standardization or data-driven conceptualization. What is your take on decision tree diagrams and do you prefer any other alternative instead? Let us know about your thoughts and experience with decision trees in the comments.