Tesla Value Chain Analysis

1. Introduction
The value chain is a series of activities conducted from the product's conception to the delivery to the customers. In other words, these are the activities that convert raw materials to the product by adding value to it to generate profit. Here, we will see the Tesla value chain analysis in detail to understand the concept and functionality of value chain analysis in a real business model.
We will see that the Tesla value chain is also based on Porter’s value chain model consisting of both primary and support activities.
2. Background of Tesla
Tesla is an innovative car manufacturing company that specializes in electric cars. It was founded in 2003 by the engineer's Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning in California, USA. The name is inspired by the 19th-century inventor Nikola Tesla, an expert in the properties of rotating electromagnetic fields.
Tesla later diversified its products and started working with solar energy products. In 2015, Tesla introduced a line of batteries to store electric power from solar energy for use in homes and businesses. Tesla Motors later changed its name to Tesla, Inc. to suggest they are no more only a car-producing company; they have more products added to their portfolio.
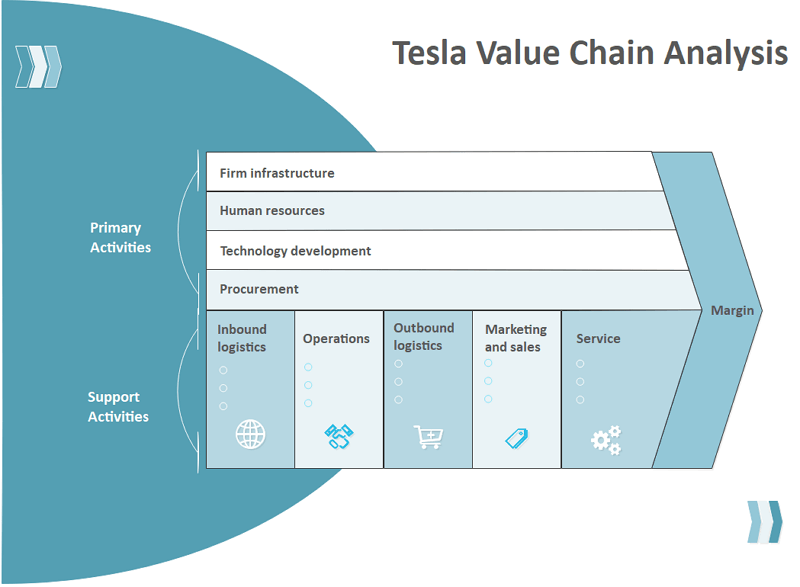
3. Primary Activities in Tesla Value Chain Analysis
Tesla's value chain analysis is based on five primary and four support activities that cooperate to gain a competitive advantage for the organization.
Source: EdrawMax OnlineInbound Logistics:
Tesla is a manufacturing company; therefore, a wide variety of raw materials is needed to produce the products. Inbound logistics include getting the raw material, storing the inputs and internally distributing the raw material and components to start production.
Since Tesla has a specialized line of products, it needs a wide range of different raw materials, including scarce materials. As a result, Tesla has a large number of suppliers worldwide. The inbound logistics need to ensure proper recordkeeping, storage and internal movement of all the inputs.
Operations:
Tesla has manufacturing plants in Fremont, California; Lathrop, California; Tilburg, Netherlands and Shanghai, China. Therefore they need both in-house operations management as well as coordination between different working units. The operations can be divided into two segments based on two different lines of products.
- Automotive that comprises design, development, manufacturing, and sales of electric vehicles.
- Energy generation and storage segment includes the design, manufacturing, installation, and sale of energy storage products and solar energy systems.
Tesla value chain analysis covers operations partly through the high integration of robots into various manufacturing processes. This high-level operation adds value to the system to gain a competitive advantage.
Outbound Logistics:
Outbound logistics include handling, warehousing, scheduling, order processing, transporting and delivery to the destination. Tesla's value chain must emphasize optimal cost and time while delivering the products and guarantee reliable products for the customers. Outbound logistics must consider customer satisfaction and guarantee it with swift and efficient transportation and delivery. This can become a good source of adding value.
Tesla also innovated the motor call sales scenario with its online sales. Tesla Motors created a multi-channel model for purchasing motor cars instead of the conventional dealership. Tesla's model includes online stores and apple-like retail outlets. Tesla promotes vertical integration on sales, which results in the non-negotiable price of vehicles.
Marketing and Sales:
Tesla motors' value chain analysis shows that the company works on the "Zero Dollar Marketing" principle. Tesla's marketing and sales depend on an unconventional model and rely on word of mouth from its satisfied customers. Tesla attracts global coverage in the media through its high quality and unique product features.
Service:
Tesla provides post-sales services at its service centers. Besides that, Tesla's value chain analysis will now include on-demand service vans throughout the country to provide quick service.
Source: Unsplash.com
4. Support Activities in Tesla Value Chain Analysis
Infrastructure:
Tesla is organized into two main divisions based on their different product categories. Therefore there are two segments of infrastructure too. However, both segments eventually came under the leadership of CEO Elon Musk. Infrastructure covers quality management, legal matters, accounting, financing, planning and strategic management. A firm infrastructure supports cost management as well.
Tesla's value chain analysis shows that the company gains competitive advantage through extensive database development to support infrastructure and advanced artificial intelligence-based information systems to get deeper customer insights.
Human Resource Management:
Tesla has to maintain its competitive advantage through the talent workforce exclusive to the organization with its innovative range of products. Here, the human resource management department works to hire, train and then retain talent.
Technology Development:
Tesla has earned a unique status in the automobile industry because of its innovative motor car technology. Hence technology development is the core of Tesla Motors' value chain analysis. This is the reason the company invested USD 1.46 billion in research and technology development. Tesla banks on innovation integration in product designing and patented technology for innovative product features. This technological innovation is the foundation of the unique status of Tesla Motors in the automobile industry.
Procurement:
Procurement and maintaining inventory of the required raw materials are the lifeline of Tesla's manufacturing process. Tesla's value chain analysis covers the procurement of thousands of parts from several different suppliers. Maintaining communication and operation with all these suppliers for smooth procurement is critical for the Tesla value chain.
Source: Unsplash.com
5. Key Takeaways
1. The first takeaway from Tesla's value chain analysis is that innovation can make a brand the leading factor in the competitive world.
2. Partnership with the suppliers to maintain inventory of the best raw material is critical for all the activities in the Tesla value chain to operate at the highest level.
3. Satisfied customers are the best and the most reliable form of marketing.
4. Even when you are a leader in one market, diversifying your product line in different markets expands your portfolio.
For a detailed and unified value chain analysis, and easy to use and efficient tool is critical. You can use EdrawMax Online for cleaner yet detailed diagrams, including value chain analysis, Porter's five forces model, organizational models, and SWOT analysis and 280+ types of diagrams. Get a quick started to analyze any business with value chain analysis examples right now.
6. References
-
John Dudovskiy. 'Tesla Value Chain Analysis', Business Research Methodology, [online]. Available at: https://research-methodology.net/tesla-value-chain-analysis-2/ (Accessed 13 Angust 2021).
-
Dale Hart, 'Value Chain: A Complete Guide to Porter’s System', The Power MBA, [online]. Available at: https://www.thepowermba.com/en/business/value-chain (Accessed 13 August 2021).